Isomerism
Isomerism
The phenomena in which compounds have same molecular formula but different structural formula is called isomerism.
e.g
propadiene
propyne
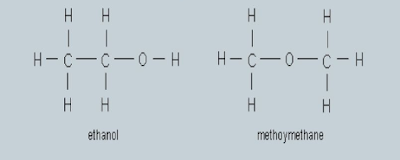
Structural Isomers
having different structural formulas because their atoms are joined together in different number of ways.
It is formed: arrangement of Carbon skeleton
e.g. The formula of C4H10 gives two possible structure, butane and methylpropane:
butane
methyl propane









Comments
Post a Comment